Complete Guide to Teak Wood: Properties, Types & Best Uses
Teak wood is renowned for its durability, resistance to water, and stunning aesthetic appeal, making it one of the most sought-after woods in the world. Commonly used in outdoor furniture, boats, and high-end flooring, teak wood holds an esteemed position due to its unique properties and versatility. Its rich golden-brown hue and natural oils contribute to its beauty and functionality, making it a favorite among woodworkers and designers alike.
In this article, we will dive deep into the world of teak wood, exploring its properties, the types of teak, the tectona grandis tree from which it comes, and much more. You'll learn about teak wood origins, where it grows, its characteristics, and its various uses, all while appreciating what makes this wood so special.
What is Teak Wood?
Teak wood is derived from the tectona grandis tree, a tropical hardwood species native to Southeast Asia. It is valued for its exceptional durability and resistance to the elements, making it ideal for outdoor applications. The wood's natural oils and rubber content provide a level of protection against moisture and pests, which is why it is often used in boat building and outdoor furniture.
The scientific name of teak is tectona grandis, and its wood is classified as a hardwood. Known for its fine grain and rich color, teak wood is not only aesthetically pleasing but also incredibly functional. The unique characteristics of teak allow it to withstand various weather conditions, making it a popular choice for materials that require longevity.
Where Does Teak Wood Grow?
Teak wood primarily grows in tropical climates, predominantly found in countries like Myanmar, Thailand, India, and Indonesia. The regions that are best suited for cultivating teak trees have a warm climate with distinct wet and dry seasons, providing the necessary conditions for healthy growth.
The teak tree typically thrives in well-drained, sandy loam soils that are rich in nutrients. As these trees mature, they can reach heights of up to 130 feet and have a trunk diameter of 3 feet or more. The teak forest is often characterized by tall, straight trees with a broad canopy, allowing for optimal sunlight penetration, which is crucial for the tree's growth.
In addition to the primary regions mentioned above, teak wood is also increasingly being cultivated in countries like Costa Rica and Brazil. These locations are now recognized for their sustainable practices in growing teak trees, contributing to the global supply while ensuring ecological balance.
Properties of Teak Wood
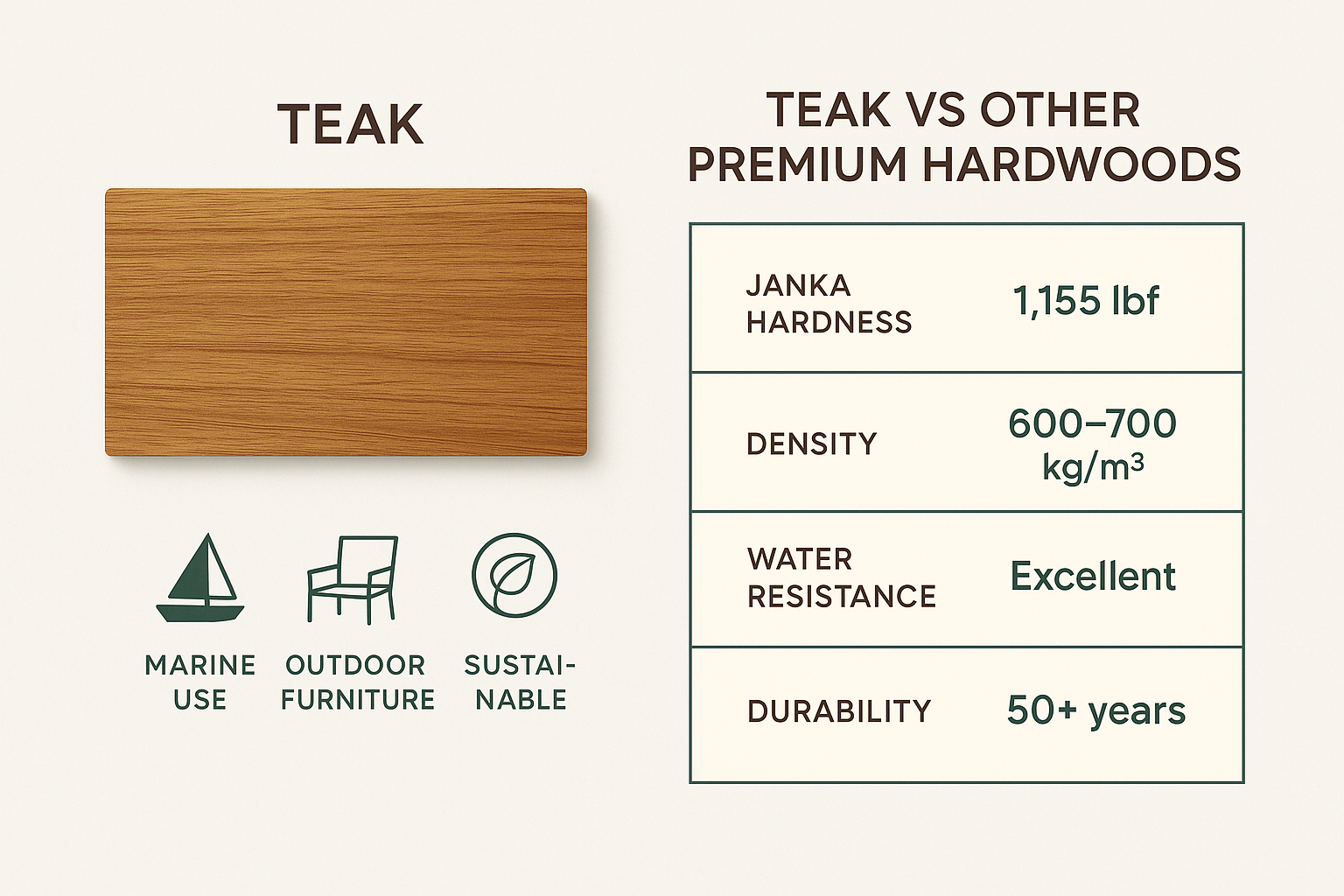
Teak Wood Properties: With a Janka hardness rating of 1,155 lbf and natural water resistance, teak outperforms many hardwoods in durability. Its 50+ year lifespan without treatment makes it ideal for marine applications and high-end outdoor furniture projects.
The properties of teak wood are numerous and contribute to its popularity in various applications. One of the standout features of teak is its natural oils, which provide resistance to moisture and prevent the wood from warping or cracking. This makes it particularly suitable for outdoor furniture and marine applications.
Furthermore, teak wood boasts a high degree of strength and durability. Its density is quite high, typically ranging around 600-700 kg/m³, which contributes to its ability to withstand wear and tear. When tested for hardness, the teak janka hardness rating is approximately 1,155 lbf, indicating that it is relatively resistant to denting and scratching.
Another notable feature is its resistance to pests, including termites and various fungi. This natural defense mechanism is essential for ensuring the longevity of teak wood products. Additionally, the wood ages beautifully, developing a silver-grey patina over time without losing its structural integrity.
Types of Teak Wood

Types of Teak Wood: Burmese teak offers the highest oil content and durability, while plantation teak provides a sustainable alternative. Each variety has distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications, from premium yacht construction to eco-friendly outdoor furniture.
There are several teak species and varieties, each with unique characteristics. While Tectona grandis is the primary teak species, different regional varieties offer distinct properties and uses. The most commonly recognized varieties include:
Burmese Teak (Tectona grandis): This is the most sought-after type due to its high oil content and rich color. Often harvested from Myanmar, it is known for its durability and resistance to rotting.
Indian Teak (Tectona grandis): Found in India, this type is slightly less dense than Burmese teak but still offers excellent durability and water resistance.
African Teak (Tectona grandis): While not as widely available, African teak is known for its attractive grain patterns and is often used in furniture making.
Plantation Teak: This refers to teak cultivated in managed forests, primarily in countries like Indonesia and Costa Rica. While it may not have the same characteristics as naturally grown teak, sustainable plantation teak can still provide good quality wood.
Each of these teak wood types offers distinct benefits, allowing consumers to choose the right type depending on their specific needs and preferences.
Teak Tree Characteristics
The teak tree is impressive not only for its wood but also for its physical characteristics. Typically, a mature teak tree can grow up to 130 feet tall and can have a trunk diameter of 3 feet or more. The leaves are large, heart-shaped, and can grow to be about 12 inches long, providing ample shade when the trees are fully leafed.
The teak tree leaf is another notable feature, as it has a rough texture and a vibrant green color that turns yellow in the autumn. This seasonal change adds aesthetic value to any landscape where teak trees are planted.
The teak flower is small and white, appearing in clusters during the flowering season. While the flowers are not particularly showy, they do attract various pollinators, contributing to the local ecosystem's health. The tectona grandis tree produces small fruits that are not typically used but can be a source of food for wildlife.
Uses of Teak Wood
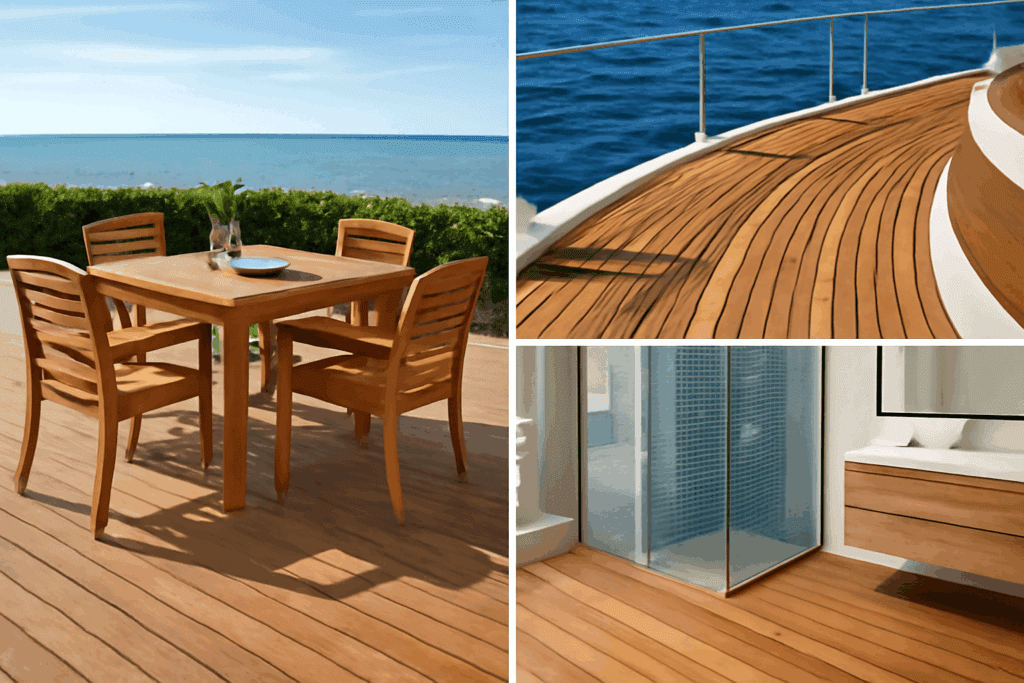

Teak Wood Applications: From luxury yacht decking to outdoor dining sets and bathroom flooring, teak's natural oils provide exceptional water resistance. These real-world applications demonstrate why teak remains the premium choice for both marine and residential projects.
The versatility of teak wood allows for a wide range of applications. One of the most popular uses is in outdoor furniture, where its natural resistance to the elements ensures longevity. Teak wood is often used for dining sets, lounge chairs, and even garden benches due to its ability to withstand rain and sun exposure.
Another significant use is in boat building. Due to its water-resistant properties, teak wood is commonly found in decking and other components of boats and yachts. The wood's ability to resist rot and decay makes it a preferred choice for marine applications.
In addition to furniture and marine use, teak wood is also utilized in flooring, cabinetry, and high-end woodworking projects. Artisans value its workability and the beautiful finish it provides, making it a favorite for custom projects and luxury items.
Teak Wood Qualities
The qualities of teak wood can be attributed to its unique composition and structure. One of the most critical qualities is its high oil content, which not only protects the wood from moisture but also gives it a natural luster. This oil helps in maintaining the wood's appearance, preventing fading and discoloration over time.
Another essential quality of teak wood is its dimensional stability. Unlike many other hardwoods, teak does not warp or crack easily, even when exposed to varying humidity levels. This makes it an ideal choice for both indoor and outdoor applications, where environmental conditions can fluctuate.
The hardness of teak is also a valuable characteristic. With a teak janka hardness rating of about 1,155 lbf, it is a strong wood that can withstand significant force. This durability makes it suitable for high-traffic areas and ensures that products made from teak wood will last for generations.
Sustainability and Conservation
With the increasing demand for teak wood, concerns about sustainability and conservation have risen. Unsustainable logging practices have led to deforestation in some regions, raising questions about the future availability of this prized wood.
Sustainable forestry initiatives aim to address these issues by promoting responsible harvesting practices. Many countries are now implementing regulations to ensure that teak trees are cultivated and harvested without compromising the ecosystem.
Plantation-grown teak wood is becoming more common as a sustainable alternative to naturally sourced timber. These plantations are often managed to ensure that the forest ecosystem is preserved while still providing a renewable source of high-quality wood.
Is Teak Endangered?
The question of whether teak is endangered is complex. While the tectona grandis tree is not currently classified as endangered, certain populations have faced significant threats due to overharvesting and habitat loss. Organizations and governments are increasingly aware of the need to protect these trees and their habitats.
In response to these concerns, conservation efforts are being put in place to ensure that teak forests are preserved for future generations. These efforts include promoting sustainable harvesting practices and reforestation projects aimed at restoring degraded forests.
Teak vs Other Premium Hardwoods
Teak vs Purpleheart Wood:
- Teak: Better water resistance, lower maintenance
- Purpleheart: More affordable, unique purple color
Teak vs Ipe Wood:
- Both excellent for outdoor use
- Teak: Easier to work with, natural oils
- Ipe: Harder (3,510 Janka vs 1,155), more affordable
Teak vs Wenge Wood:
- Teak: Better for marine applications
- Wenge: Superior for indoor furniture, darker color
Teak vs Cocobolo:
- Similar oil content and durability
- Cocobolo: More exotic grain patterns
- Teak: Better availability and sustainability
Specific Teak Wood Applications
Marine Industry:
- Yacht decking (95% of luxury yachts use teak)
- Boat railings and trim
- Marine furniture that resists saltwater
Outdoor Furniture Projects:
- Garden benches (lasts 50+ years untreated)
- Dining sets for patios and terraces
- Poolside loungers (chlorine resistant)
High-End Construction:
- Bathroom flooring (natural water resistance)
- Kitchen countertops (food-safe finish)
- Luxury hotel lobbies and spas
Specialty Woodworking:
- Musical instruments (stable in humidity changes)
- Cutting boards (natural antibacterial properties)
- Tool handles (comfortable grip, durable)
Frequently Asked Questions About Teak Wood
Q: Is teak wood worth the investment?
A: Yes, teak's 50+ year lifespan and minimal maintenance make it cost-effective long-term compared to other hardwoods that need regular treatment.
Q: Is teak a hardwood or softwood?
A: Yes, teak is classified as a hardwood. Despite its workability, teak comes from the deciduous Tectona grandis tree, making it a true hardwood with a Janka rating of 1,155 lbf.
Q: How does teak compare to ipe wood for outdoor use?
A: While ipe is harder, teak's natural oils make it easier to maintain and work with, making it preferred for marine applications.
Q: Can you use teak indoors?
A: Absolutely. Teak excels in bathrooms, kitchens, and high-humidity areas where other woods would warp or rot.
Q: What's the difference between plantation and old-growth teak?
A: Old-growth teak (like Burmese) has higher oil content and tighter grain, but sustainable plantation teak offers 80% of the benefits at lower cost.
Explore More About Wood: