Basswood Wood: Complete Guide to Properties and Uses
Basswood, scientifically known as Tilia americana, is a deciduous tree native to North America. It belongs to the Tilia genus and is well-known for its light, soft wood, making it a favorite among woodworkers and craftsmen. Basswood is often sought for its versatility and ease of use, especially in applications where fine detail work is required. The tree itself is notable for its broad leaves, fragrant flowers, and valuable ecological contributions, including providing habitat and food for various wildlife.
In this article, we will explore various aspects of basswood, including its characteristics, uses, and health benefits. We will also clarify common questions such as is basswood a hardwood or softwood, its density, and how it compares to other types of wood, including balsa wood. Whether you're a woodworking enthusiast, a student of botany, or simply curious about this remarkable tree, you will find a wealth of information in the sections that follow.
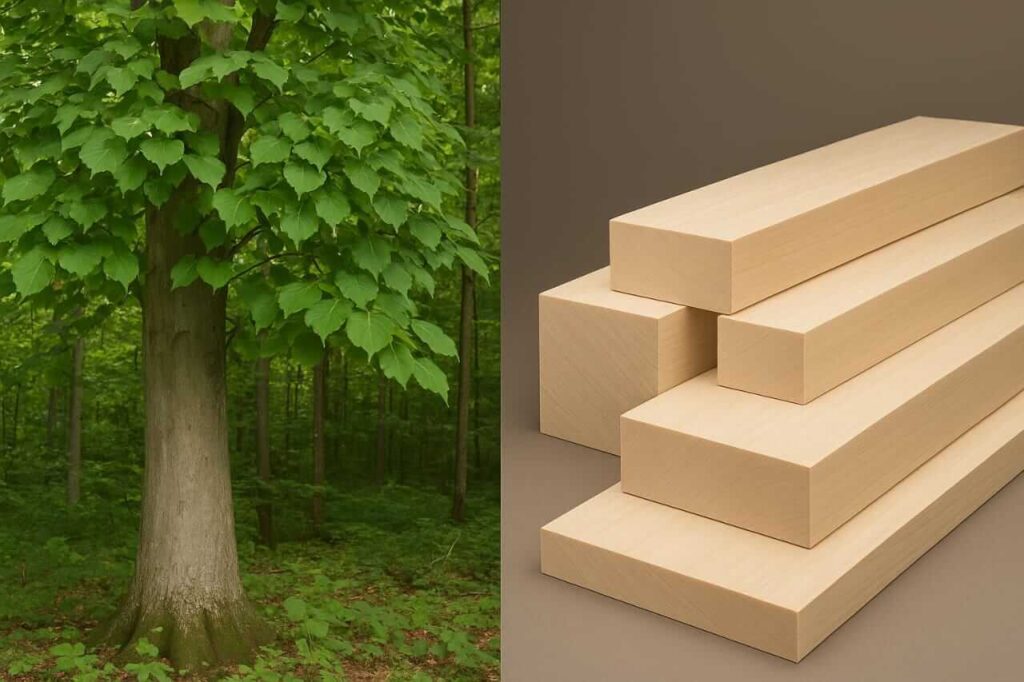

What Is Basswood?
To define basswood, we begin by understanding its characteristics and classification. Basswood refers to several species in the Tilia genus, with the most common being Tilia americana, known as American basswood. This tree typically grows to heights of 60-80 feet and has a broad, rounded crown. The bark is smooth and gray, while the leaves are heart-shaped, with serrated edges.
The wood of the basswood tree is light in color, with a fine and even grain. It is often described as creamy white or pale yellow, making it aesthetically pleasing for various applications. One of the most notable characteristics of basswood is its softness. In fact, when discussing how hard is basswood, it’s essential to note that it has a low Janka hardness rating of about 410 lbf (pounds-force), which is significantly softer than many hardwoods.
The softness of basswood is one reason it is favored for intricate carving and detailed work. Its ease of manipulation allows woodworkers to create finely detailed pieces without the strain that harder woods might impose. Additionally, basswood lumber is often used in model-making, musical instruments, and even toys due to its favorable working properties.
Characteristics of Basswood
Physical Attributes
The basswood tree is characterized by its tall stature, reaching heights of up to 100 feet in some cases, with a trunk diameter of around 2-3 feet. The leaves are typically 4-8 inches long and are dark green on the upper side and paler underneath. During spring and summer, basswood trees produce clusters of small, fragrant, yellowish-white flowers that attract pollinators like bees.
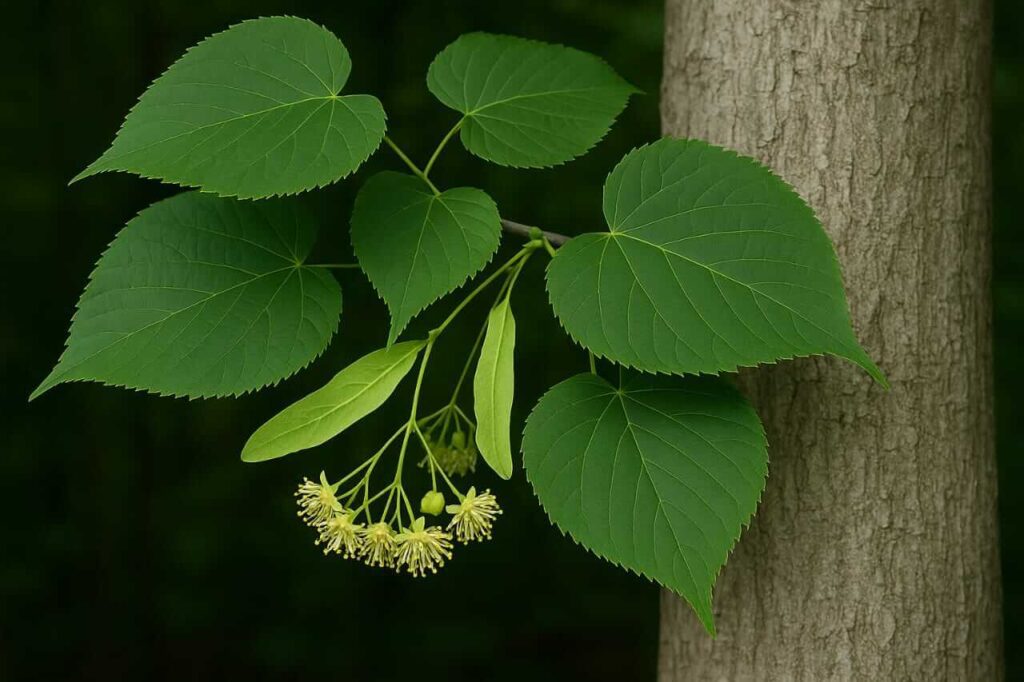

The basswood tree bark is smooth and gray when young, but as it ages, it can develop fissures and a rough texture. The tree's flowers are hermaphroditic, meaning they contain both male and female reproductive organs, supporting its reproductive cycle. The fruit of the basswood tree, often referred to as basswood fruit, is a small, round nutlet that is not widely consumed by humans but serves as food for birds and small mammals.
Density and Hardness
When discussing wood, density is an important factor that influences its durability and strength. The density of basswood is relatively low, typically ranging from 25 to 30 pounds per cubic foot, making it one of the lightest hardwoods available. This characteristic makes it ideal for applications where weight is a consideration, such as in the construction of musical instruments or in model making.
In terms of strength, one might wonder is basswood strong enough for various projects. While it is not known for its strength compared to denser hardwoods, it is still suitable for many applications, particularly where intricate detail is required rather than structural strength. Woodworkers often appreciate how basswood's softness allows for detailed carving without excessive wear on tools.
Growth and Range
Where does basswood grow? Basswood is primarily found in the eastern United States and Canada, thriving in rich, moist, and well-drained soils. It prefers full sunlight but can also grow in partial shade. The basswood tree range extends from southern Ontario and Quebec in Canada down through the Midwest and into parts of the southeastern U.S., including states like Ohio, Kentucky, and Tennessee.
In terms of climate, basswood prefers temperate regions with distinct seasons, which contributes to its growth cycle and overall health. It is commonly found in mixed forests, often growing alongside oaks, maples, and hickories. The American basswood tree has a significant role in forest ecosystems, providing shelter and food for various species of wildlife, including birds and insects.
Uses for Basswood
Woodworking and Carving
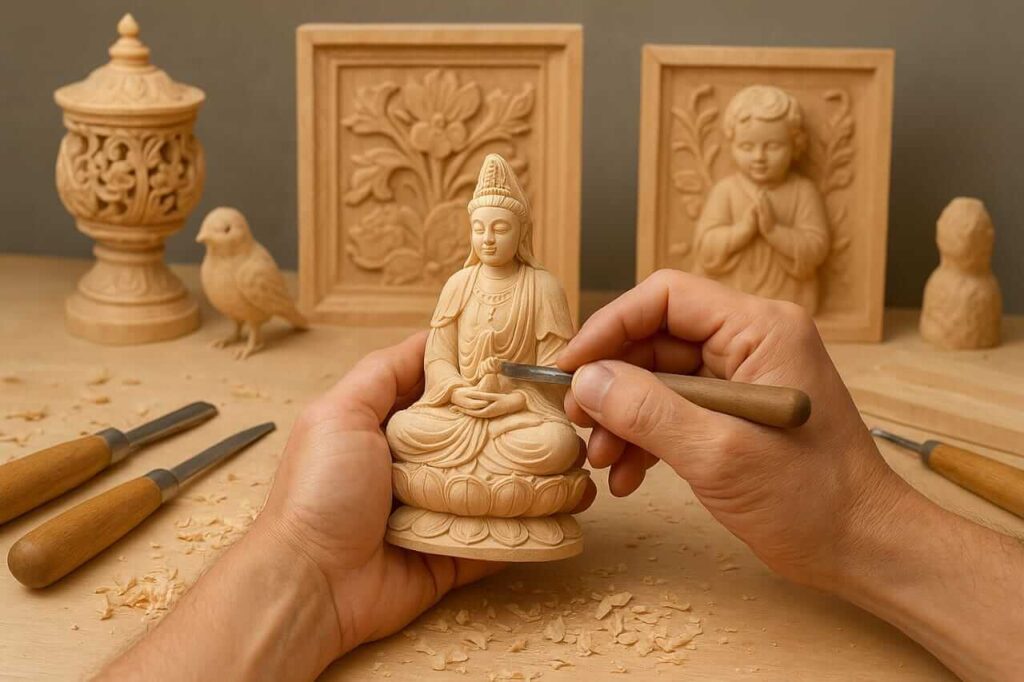
One of the most popular uses for basswood is in the realm of woodworking. Its soft, light nature makes it particularly amenable to carving, allowing artisans to create intricate designs and detailed representations. Basswood woodworking is a favorite among hobbyists and professionals alike, especially for crafting figurines, toys, and decorative items.
Due to its fine grain, basswood accepts paint and finishes exceptionally well, making it a versatile choice for artists and craftsmen. When considering what is basswood good for, the answer often points to its suitability for projects where detail and finish are paramount. Additionally, basswood dimensional lumber is readily available, making it accessible for various woodworking projects.
Musical Instruments
Basswood is also widely used in the production of musical instruments. Its light weight and tonal properties make it an excellent choice for crafting guitars, ukuleles, and other string instruments. When discussing what is basswood used for, one cannot overlook its importance in the music industry. Luthiers often select basswood for its ability to produce a warm, resonant sound while remaining lightweight and easy to work with.
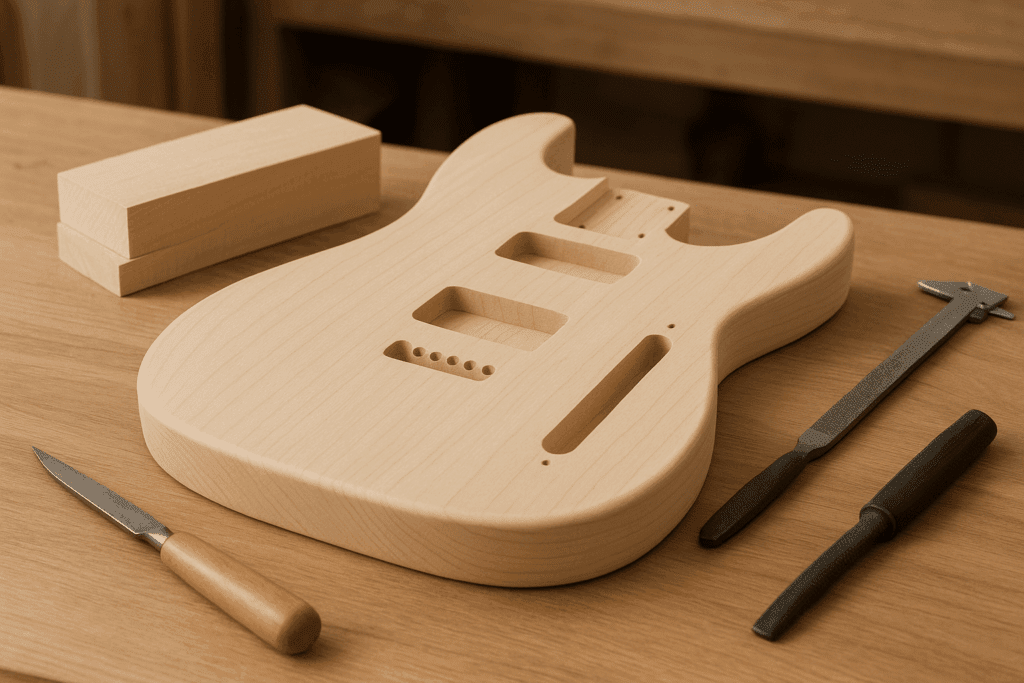

The wood's acoustic qualities can enhance the tonal characteristics of instruments, leading to a more pleasing sound. Additionally, basswood's soft texture allows for easier shaping and sanding, which is crucial in the instrument-making process. For this reason, many entry-level electric guitars feature bodies made from basswood, making it an accessible option for aspiring musicians.
Model Making and Crafts
Beyond traditional woodworking and musical instruments, basswood has found a niche in model making. The wood's light weight and ease of cutting make it an ideal material for creating scale models, architectural designs, and hobby crafts. Many model builders prefer basswood because it can be easily shaped and glued, allowing for precision in their creations.
In addition to model making, basswood is often used in DIY crafts and projects. Its affordability and availability in various sizes and shapes make it a go-to choice for home crafters and educators. Teachers often use basswood in art and craft projects for students, as it is easy to manipulate and safe to work with, fostering creativity and skill development.
Health Benefits of Basswood Trees
Ecological Contributions
The basswood tree health benefits extend beyond just its wood. As a deciduous tree, basswood plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. Its broad leaves provide shade and habitat for various wildlife species, including birds, insects, and small mammals. During the flowering season, the tree attracts pollinators such as bees, which are essential for the reproduction of many plant species.
Moreover, basswood trees can improve air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. This makes them valuable assets in urban forestry and land restoration projects. The presence of basswood in a landscape can contribute to biodiversity, providing food and shelter for a variety of organisms.
Medicinal Uses
Historically, various parts of the basswood tree have been utilized for medicinal purposes. The flowers, in particular, have been used to make herbal teas that are thought to have calming properties. These teas are often consumed to promote relaxation and alleviate anxiety, making them a popular choice for individuals seeking natural remedies.
The inner bark of the basswood tree has also been traditionally used by indigenous peoples for its medicinal properties. It is believed to have anti-inflammatory and soothing effects, and some cultures have used it to treat ailments such as fevers and respiratory issues. While modern scientific validation of these uses is limited, they highlight the historical significance of basswood in traditional medicine.
Aesthetic and Cultural Value
Beyond its ecological and medicinal benefits, basswood also holds aesthetic and cultural value. Its beautiful flowers and lush foliage make it a popular choice for landscaping and ornamental purposes. Many homeowners and landscapers appreciate basswood for its ability to provide shade and enhance the beauty of outdoor spaces.
In some cultures, the basswood tree is seen as a symbol of strength and resilience. Its presence in community spaces can foster a sense of connection to nature and promote mental well-being. The tree's importance in traditional crafts and folklore further highlights its cultural significance in various regions.
How Basswood Compares to Other Hardwoods
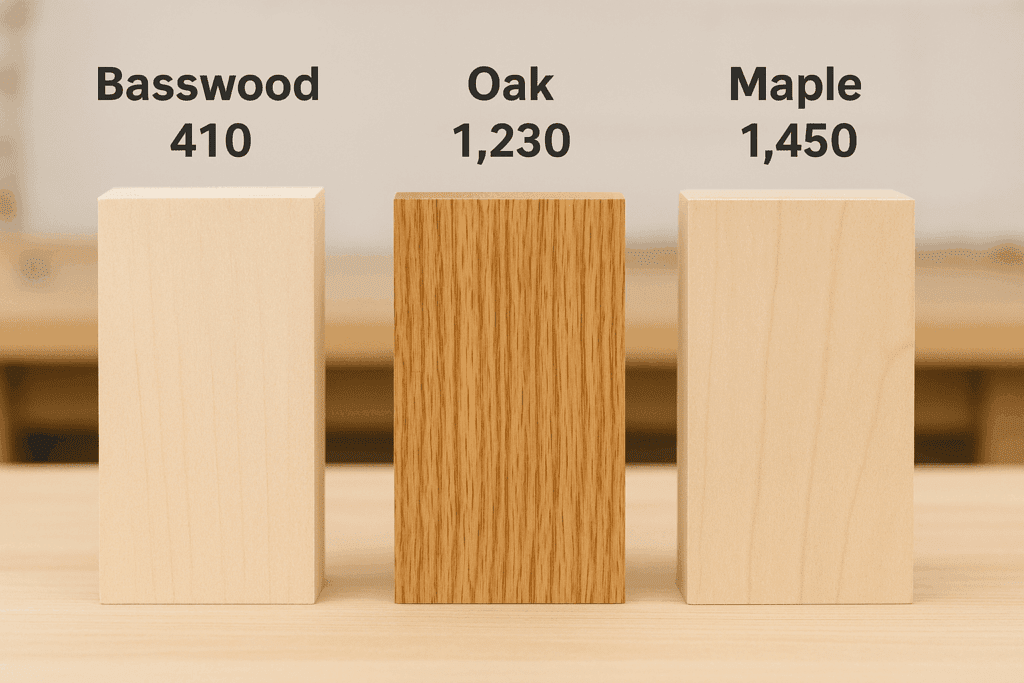
- Basswood vs Oak While oak (Janka: 1,360 lbf) excels in structural applications, basswood's softness makes it superior for detailed work. Oak's pronounced grain can interfere with fine carving, whereas basswood's subtle grain provides a clean canvas for artisans.
- Basswood vs Maple Curly maple offers stunning figure but requires more skill to work. Basswood's consistent density eliminates the tear-out issues common with maple's alternating grain patterns, making it ideal for beginners.
- Basswood vs Tropical Hardwoods Unlike dense tropical species such as teak or ipe wood, basswood doesn't require specialized tools or cause rapid tool dulling. This makes it more accessible for hobbyists and educational use.
- Basswood vs Softwoods Traditional softwoods like pine contain resin that can interfere with finishes. Basswood offers the workability of softwood without resin bleeding, making it superior for painted projects.
Why Choose Basswood Over Alternatives
- For carving: Easier than purpleheart wood or wenge wood
- For instruments: More affordable than sapele with similar tonal qualities
- For beginners: More forgiving than exotic woods like cocobolo
When to Choose Other Woods Instead
Consider alternatives like mango wood for outdoor projects or olive wood when distinctive grain patterns are desired.
Frequently Asked Questions About Basswood
What is basswood?
Basswood is a soft hardwood from the Tilia americana tree, native to North America. Despite being classified as hardwood, it has a low Janka hardness rating of 410 lbf, making it extremely workable for detailed carving and crafts.
Is basswood a hardwood or softwood?
Technically, basswood is a hardwood because it comes from a deciduous tree. However, with its soft texture and low density (25-30 lbs/ft³), it behaves more like a softwood in practical woodworking applications.
What is basswood used for?
Basswood is primarily used for:
- Intricate wood carving and whittling
- Musical instrument bodies (guitars, ukuleles)
- Model making and architectural models
- Educational craft projects
- Decorative items and figurines
- Toy manufacturing
How does basswood compare to balsa wood?
While both are lightweight, basswood is denser and more durable than balsa wood. Basswood offers better strength for detailed carving, while balsa is primarily used for ultra-light applications like model aircraft.
Real-World Applications of Basswood
- Professional Wood Carving Master carvers like those creating nativity scenes or decorative architectural elements prefer basswood for its consistent grain and minimal tool wear. The wood's softness allows for intricate details like facial features or delicate foliage without splitting.
- Guitar Manufacturing Entry-level electric guitars from brands like Yamaha and Ibanez often feature basswood bodies. The wood provides balanced tone characteristics while keeping manufacturing costs reasonable for beginner instruments.
- Educational Settings Art teachers favor basswood for student projects because it's safe to work with and forgiving of mistakes. Students can easily carve soap-like sculptures or create relief panels without requiring professional-grade tools.
- Model Railroad Hobbyists Scale model builders use basswood strips and sheets to construct detailed buildings, bridges, and scenic elements. Its light weight prevents overloading delicate model structures while maintaining realistic proportions.
- Prototype Development Product designers often use basswood for creating functional prototypes of consumer goods, furniture components, or architectural details before moving to final materials.

Explore More About Wood: